Home Sweet Home: Tips for Accurate Blood Pressure Monitoring at Home
The BPHub Team
2025-03-29

High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common condition that can lead to serious health complications if not managed properly. Monitoring your blood pressure at home is a crucial step in managing this condition effectively. Not only does it help you keep track of your health, but it also provides valuable information to your healthcare provider. In this blog post, we will explore the best practices for accurate blood pressure monitoring at home, ensuring you get the most reliable readings possible.
Understanding the Importance of Home Blood Pressure Monitoring
Home blood pressure monitoring is an essential tool for managing hypertension. It allows individuals to track their blood pressure regularly, providing a more comprehensive picture of their cardiovascular health. According to the Mayo Clinic, regular monitoring can help detect patterns and fluctuations that might not be apparent during occasional visits to the doctor [1]. This continuous data can be invaluable in adjusting medications and lifestyle changes to better control blood pressure.
Benefits of Home Monitoring
- Early Detection: Regular monitoring can help detect hypertension early, allowing for timely intervention.
- Better Management: Continuous data helps in adjusting treatment plans effectively.
- Reduced Anxiety: Monitoring at home can reduce anxiety associated with "white coat syndrome," where blood pressure readings are higher in a clinical setting.
- Empowerment: It empowers individuals to take charge of their health and make informed decisions.
Choosing the Right Blood Pressure Monitor
Selecting the right blood pressure monitor is the first step in ensuring accurate readings. There are several types of monitors available, including arm cuff, wrist cuff, and finger models. Each type has its pros and cons, and the choice largely depends on personal preference and specific health needs.
Types of Blood Pressure Monitors
- Arm Cuff Monitors: These are the most common and generally considered the most accurate. They are recommended by healthcare professionals for home use [2].
- Wrist Cuff Monitors: While convenient, they can be less accurate if not positioned correctly. It's crucial to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully [5].
- Finger Monitors: These are the least accurate and are not generally recommended for home monitoring.
Tips for Choosing a Monitor
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Before purchasing a monitor, discuss with your healthcare provider to determine the best option for your needs.
- Look for Validated Devices: Ensure the monitor is clinically validated for accuracy.
- Consider Ease of Use: Choose a device that is easy to use and understand, especially if you have limited experience with technology. Some new devices even include Bluetooth technology for connecting to a cellphone and thus providing better experience.
Preparing for Accurate Blood Pressure Measurement
To obtain accurate readings, proper preparation is essential. Several factors can influence blood pressure readings, including stress, caffeine, and physical activity. Here are some tips to prepare for an accurate measurement:
Pre-Measurement Tips
- Avoid Caffeine and Tobacco: Refrain from consuming caffeine or using tobacco products at least 30 minutes before measuring your blood pressure.
- Rest Before Measurement: Sit quietly for at least five minutes before taking a reading.
- Use the Bathroom: Ensure your bladder is empty, as a full bladder can affect readings.
- Maintain a Consistent Schedule: Measure your blood pressure at the same time each day for consistency.
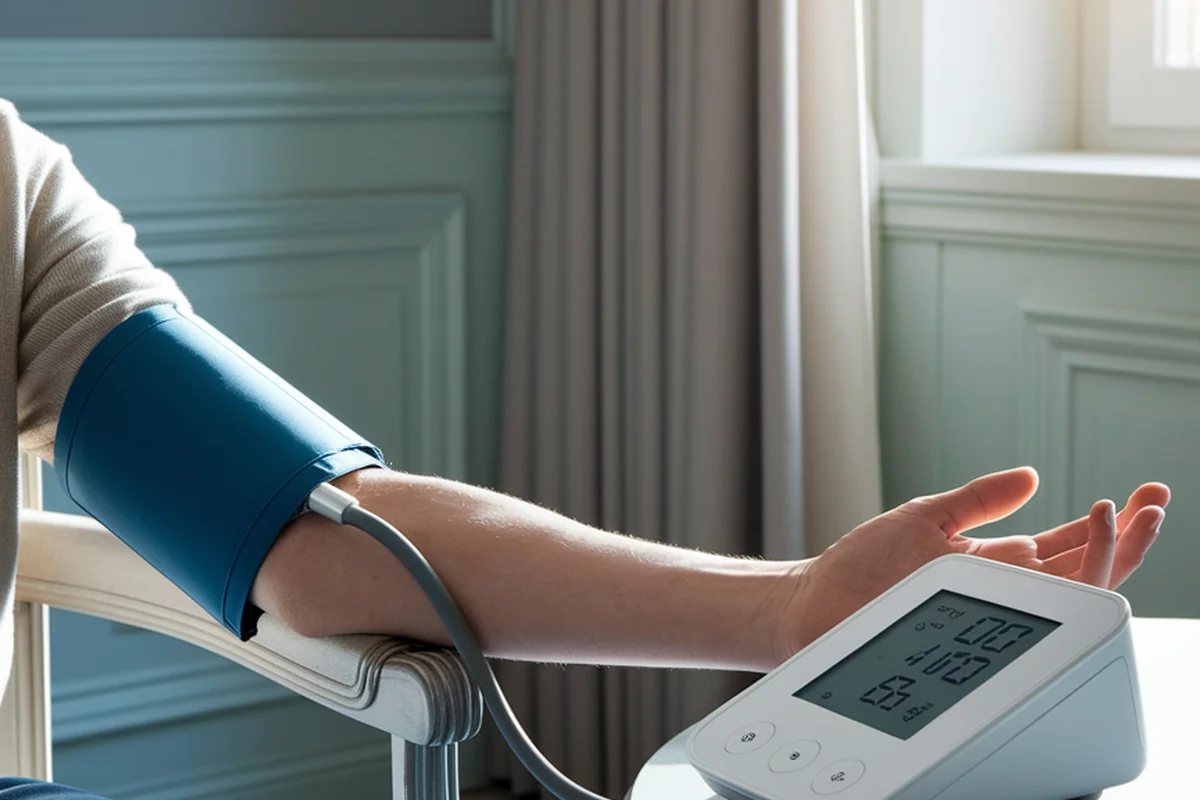
Taking the Measurement: Step-by-Step Guide
Once you are prepared, follow these steps to ensure an accurate blood pressure reading:
Step-by-Step Process
- Sit Correctly: Sit in a chair with your feet flat on the floor and your back supported. Keep your arm at heart level.
- Position the Cuff Properly: If using an arm cuff, place it on your bare upper arm, about an inch above the elbow. Ensure it's snug but not too tight.
- Stay Still and Silent: Avoid talking or moving during the measurement.
- Take Multiple Readings: Take two or three readings, one minute apart, and calculate the average for a more accurate result. Many people find that the first reading is the highest, and that after 5 to 10 minutes the blood pressure stabilizes in lower levels.
- Record Your Readings: Keep a log of your readings, including the date and time, to share with your healthcare provider.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the best intentions, mistakes can occur during home blood pressure monitoring. Here are some common pitfalls and how to avoid them:
Mistakes to Avoid
- Incorrect Cuff Size: Using a cuff that is too small or too large can lead to inaccurate readings. Ensure the cuff fits your arm properly.
- Improper Arm Position: Keep your arm at heart level to avoid skewed results.
- Ignoring Device Calibration: Regularly check that your device is calibrated correctly, as per the manufacturer's instructions.
- Not Following Instructions: Always follow the device's instructions carefully to ensure accuracy.
Interpreting Your Blood Pressure Readings
Understanding your blood pressure readings is crucial for effective management. Blood pressure is recorded as two numbers: systolic and diastolic. The systolic pressure (the higher number) measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats, while the diastolic pressure (the lower number) measures the pressure between beats.
What Do the Numbers Mean?
- Normal: Less than 120/80 mm Hg
- Elevated: Systolic between 120-129 and diastolic less than 80
- Hypertension Stage 1: Systolic between 130-139 or diastolic between 80-89
- Hypertension Stage 2: Systolic at least 140 or diastolic at least 90
- Hypertensive Crisis: Systolic over 180 and/or diastolic over 120, requiring immediate medical attention
When to Consult Your Healthcare Provider
While home monitoring is an excellent tool for managing blood pressure, it's important to know when to seek professional advice. If you consistently get readings that are higher than normal, or if you experience symptoms such as dizziness, headaches, or shortness of breath, consult your healthcare provider immediately.
Conclusion
Accurate blood pressure monitoring at home is a vital component of managing hypertension effectively. By choosing the right monitor, preparing properly, and avoiding common mistakes, you can ensure reliable readings that will help you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your health. Remember, while home monitoring is beneficial, it should complement regular check-ups with your healthcare provider.
For personalized medical advice, always consult with a healthcare professional.
References
- Mayo Clinic. Get the most out of home blood pressure monitoring. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/in-depth/high-blood-pressure/art-20047889
- AARP. 5 Tips to Measure Blood Pressure Accurately at Home. Retrieved from https://www.aarp.org/health/conditions-treatments/info-2019/home-blood-pressure-monitoring.html
- Mayo Clinic. 10 ways to control high blood pressure without medication. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/in-depth/high-blood-pressure/art-20046974
- Wirecutter. New Product Reviews, Deals, and Buying Advice. Retrieved from https://www.nytimes.com/wirecutter/
- Mayo Clinic. Wrist blood pressure monitors: Are they accurate? Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/expert-answers/wrist-blood-pressure-monitors/faq-20057802
This blog was created by the BPMaestro Team under the supervision of Santiago Miriuka, MD PhD.
